In bicycles with hydraulic disc brakes, instead of the cable rope, there is hydraulic oil inside the outer cable, thus preventing the friction of the brake wire on the outer cable and squeezing the brakes thanks to the oil pressure. Hydraulic brakes are applied more smoothly than other brakes. The force applied by the fingers is less.
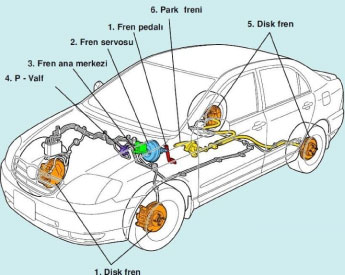
The system that is used to slow down or stop a moving vehicle and to keep a stationary vehicle in place is called the brake system. The total movement energy of the vehicle is converted into heat energy generated by the friction of the pads against the disc and the vehicle stops. (KE=1/2 mV2) There are two types of friction that explain the working mechanism of brake systems; kinetic (moving) and static (still).
When braking, kinetic friction occurs in the friction elements and static friction occurs between the tire and the road, thus slowing the vehicle.
In hydraulic brakes, hydraulic oil pressure is used to operate the braking organs of the vehicle. When force is applied to the pedal in the brake system, the piston of the master cylinder creates pressure. This pressure is transmitted to the wheel cylinders by means of pipes. By opening the pistons of the wheel cylinders, braking is provided. Hydraulic brake systems are mostly used in passenger cars. Its response time is shorter than other systems. It is easier to manufacture and cheaper as a system.
The operation of an automobile braking system is based on two fundamental physics principles.

A fluid in a closed system transmits the applied pressure equally in all directions.
Energy cannot be created out of nothing; cannot be destroyed in existing energy. But it can be converted into other forms of energy.
According to Pascal's principle, a pressure change occurring in any part of an incompressible fluid placed in a container is transmitted by the liquid to every point of the inner surfaces of the container, regardless of the shape of the container. Liquids are used in the transmission of motion and force. Liquids are incompressible fluids. Because there is less space between the molecules of liquids. Air is compressible. Therefore, the air in the system will cause insufficient braking.
Pressure builds up when a force acts on an area. Formula: Pressure = Force / cross-sectional area ( P = F / A ) The pressure active in the brake center pump is transferred to all wheel cylinders in equal amounts. The braking force will vary depending on the diameter of the wheel cylinders. If we want more braking force on the front wheels of the vehicle, the front cylinder should be larger than normal.



Janet Lopez